Irregular Korean Verbs With ‘르’ (르 불규칙)
In this lesson, you will learn how to conjugate irregular verbs with 르 (르 불규칙). In a previous lesson, you learned about ㅡ irregular verbs. Although 르 irregular verbs also end in ㅡ, they are different and follow different conjugation rules.
Below you will find a list of 르 irregular verbs and will learn how to conjugate irregular verbs with 르.
르 Irregular (르 불규칙)
Verbs and adjectives that end in 르 are irregular. This means that when they are conjugated with various endings, they do not follow the normal conjugation rules. For example, the adjective 빠르다 (to be fast) ends in 르 and so it is irregular. When conjugating 빠르다 in the present tense it becomes 빨라요 and not 빨르어요.
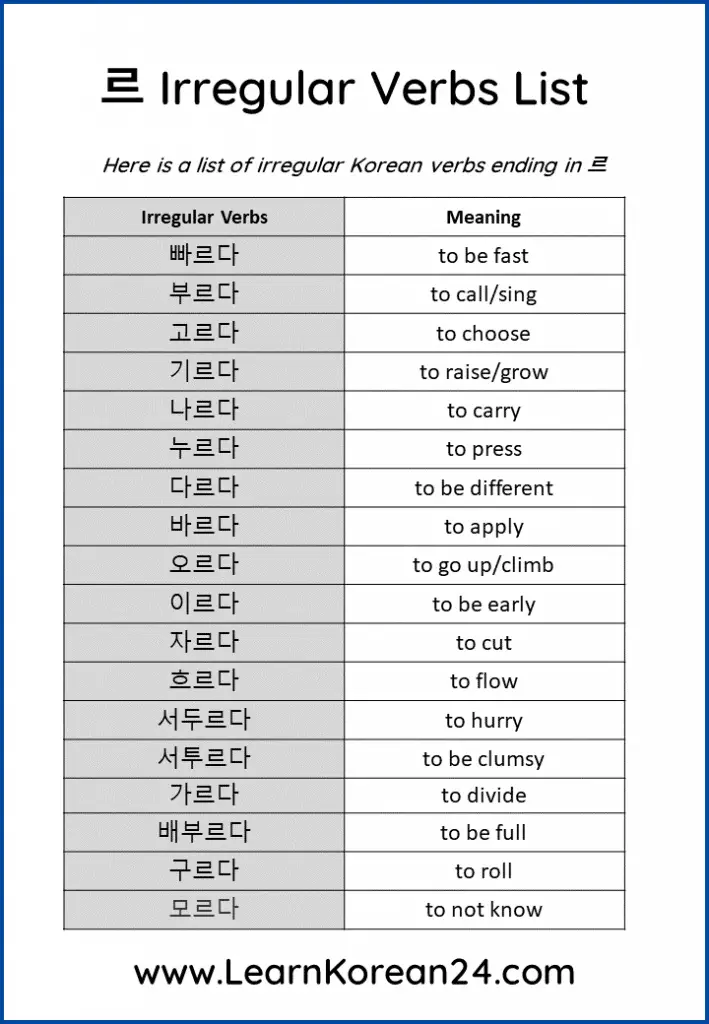
Here is a list of 르 irregular verbs in Korean (르 불규칙):
- 빠르다 = to be fast
- 부르다 = to call/sing
- 고르다 = to choose
- 기르다 = to raise/grow
- 나르다 = to carry
- 누르다 = to press
- 다르다 = to be different
- 바르다 = to apply
- 오르다 = to go up/climb
- 이르다 = to be early
- 자르다 = to cut
- 흐르다 = to flow
- 서두르다 = to hurry
- 서투르다 = to be clumsy
- 배부르다 = to be full
- 가르다 = to divide
- 구르다 = to roll
- 모르다 = to not know
How To Conjugate ‘르’ Irregular Verbs (르 불규칙)
If you have read the previous lesson about ㅡ irregular verbs, then learning how to conjugate 르 irregular verbs is not very difficult. Here are the key things to remember when conjugating irregular verbs that end in 르:
1. Irregular verbs and adjectives ending in 르 only behave irregularly when an ending starting with 아 or 어 is attached.
For example, endings such as 아요/어요 (present tense), 았어요/었어요 (past tense), etc, start with 아 or 어. So, when these endings are attached to 르 irregular verbs and adjectives it makes them behave irregularly. That is to say, they are conjugated differently than regular verbs and adjectives.
When 르 irregular verbs and adjectives are conjugated with endings which do not start with 아 or 어, they do not behave irregularly and are just conjugated the same as normal verbs and adjectives.
2. When conjugating irregular 르 verbs and adjectives with endings starting with 아 or 어, ㅡ is always dropped and an additional ㄹ is added.
Take the verb 모르다, for example. When conjugated in the present tense, 모르다 becomes 몰라요. This is because ㅡ is dropped and an additional ㄹ is added before the ending 아요.
3. The vowel that comes before 르 determines whether 아 or 어 is used in the ending.
For example, when you want to conjugate an irregular 르 verb with the ending 아서/어서 (so), you must choose to add 아서 or 어서. The one you should choose is determined by the vowel which precedes 르 in the verb/adjective stem.
If the vowel before 르 is ㅏ or ㅗ, then the ending starting with 아 should be used.
For example, the vowel before 르 in 빠르다 (to be fast) is ㅏ. So, the ending starting with 아 should be used.
빠르다 = to be fast
빨라요 = fast (present tense)
빨랐어요 = was fast (past tense)
빨라서… = fast, so…
If the vowel before 르 is NOT ㅏ or ㅗ, then the ending starting with 어 should be used.
For example, the vowel before 르 in the verb 부르다 (to sing/call) is ㅜ. As this is not ㅏ or ㅗ, we should choose the ending starting with 어.
부르다 = to sing/call
불러요 = sing/call (present tense)
불렀어요 = sang/called (past tense)
불러서… = sing, so…
4. The last thing to know about 르 irregular verbs is that there are a few exceptions.
There are a few exceptions to the above conjugation rules. The following verbs all look like irregular 르 verbs, but they are actually irregular ㅡ verbs. And so they should be conjugated the same way as irregular ㅡ verbs (i.e. no additional ㄹ is added).
따르다 = to follow
치르다 = to pay
들르다 = to drop in
Irregular 르 Examples
Here are some examples of irregular verbs and adjectives that end in 르 conjugated with some common endings.
Irregular 르 Example Sentences
Here are some example sentences which include irregular 르 verbs.
- BTS 를 정말 몰라요? (모르다) = You really don’t know BTS?
- 제 친구는 화초를 길러요. (기르다) = My friend grows plants.
- 머리를 얼마나 자주 잘라요? (자르다) = How often do you get your haircut?
- 택시가 버스보다 더 빨라요. (빠르다) = Taxis are faster than buses.
- 목이 아파서 노래를 못 불러요 (부르다) = I have a sore throat so I can’t sing.
More Korean Irregular Verb Lessons
There are seven types of irregular verbs in Korean. For more lessons on Korean Irregular verbs, click on the links below.
ㅂ Irregular
ㅡ Irregular
르 Irregular
ㄷ Irregular
ㄹ Irregular
ㅅ Irregular
ㅎ Irregular
STUDY ONLINE WITH KOREAN ARAH!
Ready to take your Korean to the next level?
Get One-on-One Korean lessons from a qualified and experienced Korean language tutor!